High Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) and Heart Health

You may have heard of a type of exercise called high-intensity interval training or HIIT. It involves short bursts of intense activity alternating with less-intense activity or rest and is being studied for its effectiveness in improving overall fitness and heart health.
What Are the Benefits of Interval Training?
Young, healthy people may benefit from interval training for heart health. If you’re older, starting an exercise regimen after a period of being sedentary, or have heart disease or other serious medical conditions, you should consult your doctor before trying HIIT.
One of the main draws of high-intensity interval training is that you may be able to improve your fitness faster. Studies suggest that HIIT exercise can deliver improvements in blood sugar and blood pressure management equal to or greater than moderate-intensity exercise. This approach may be helpful for people who have busy lives but want to stay fit.
That being said, many factors affect whether HIIT is right for you. In addition to your age and medical history, there are considerations like whether your muscles, joints, etc., can endure the force of a high-intensity workout. So, again, you should talk with our physician before starting a high-intensity exercise program.
Common HIIT Modes
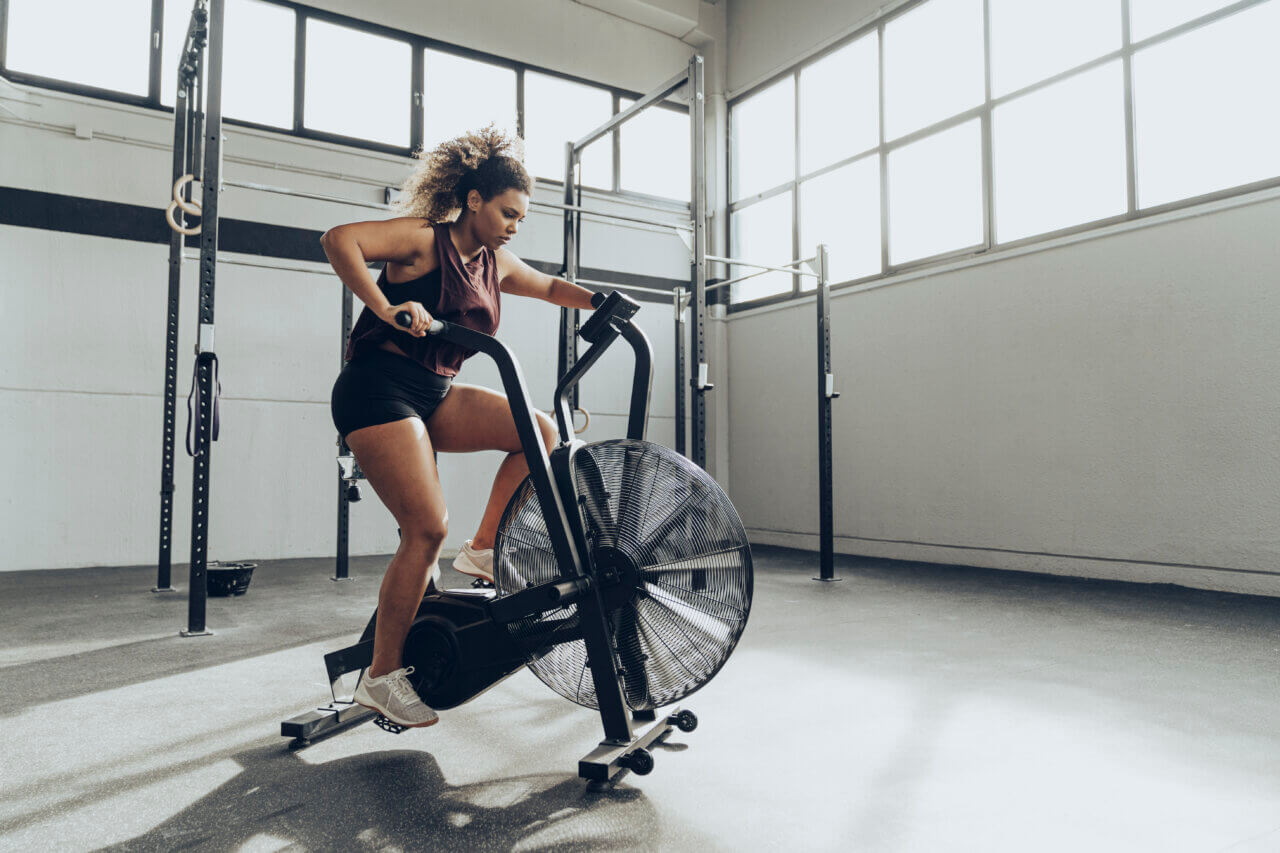
Many types of exercise that use large muscle groups, like those in the legs, can be performed in HIIT mode. People will commonly develop HIIT workouts that incorporate:
- Stationary biking
- Swimming
- Road biking
- Using an elliptical machine
- Running
- Walking uphill
The sessions typically involve intense exercise periods of 10 to 60 seconds followed by recovery intervals that are equal or longer. This may be repeated 3 to 10 times, depending on the person’s current fitness level, fitness goals, etc.
HIIT vs. Cardio for Heart Health
Which is better: HIIT or steady-state cardio exercise? Each has its pros and cons. The advantages of HIIT include that it’s a shorter workout, creates more post-workout calorie burn, and can result in improved heart health and insulin sensitivity. The disadvantages are that there’s a higher injury risk, it can be uncomfortable, and it’s not recommended for beginners.
Steady-state cardio workouts improve overall health and endurance with less stress on your heart, lungs, and muscles in general. It may also be more enjoyable and requires less recovery time. On the downside, cardio is time-consuming, can be boring or monotonous, and increases the risk of overuse injuries.
Consequently, many people utilize a mix of HIIT and steady-state cardio to pursue their fitness goals.
HIIT and Heart Patients
The cautions about starting HIIT workouts are warranted. However, there are studies showing that HIIT can be safe for older people and even heart and stroke patients when conducted in a supervised healthcare setting. More research is needed, but it appears that the body can tolerate and benefit from a certain amount of intense activity.
Talk with Your Baptist Health Physician About High-Intensity Interval Training
If you’re interested in using high-intensity interval training, your Baptist Health physician is happy to talk with you about your fitness goals and how to achieve them safely. And if you’ve had a heart attack or have other heart-related issues, your doctor can refer you to our heart care specialists.