Health Benefits of Eggs
In the past, eggs have been associated with negative health effects, mainly due to their cholesterol content. However, we now know blood cholesterol levels are influenced by many factors — not just dietary cholesterol. Contrary to this common misconception, eggs are highly nutritious and contain many important nutrients and vitamins. Studies have also shown that eating an egg a day can help lower the risk of stroke.
Important Nutrients Found In Eggs
Here’s a breakdown of just some of the good-for-the-body contents of eggs.
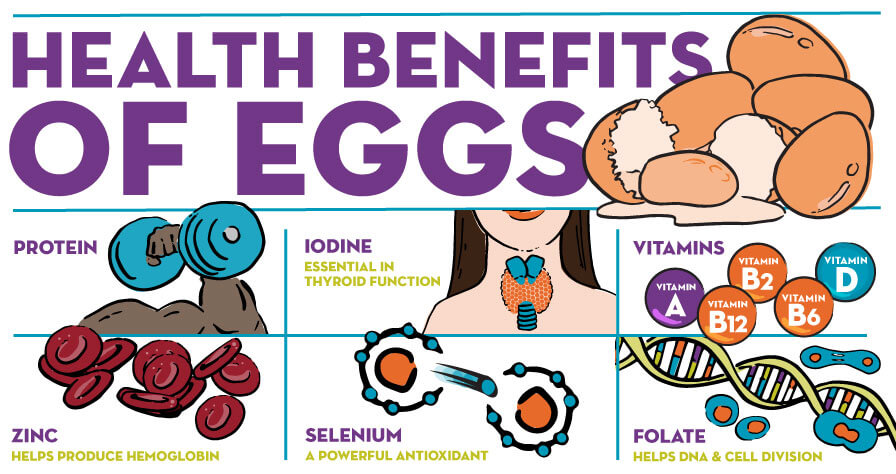
Protein. Eggs are an inexpensive source of protein. In two medium eggs, there are 11.8 grams of protein. That amounts to 18% of the recommended daily protein intake. And, eggs are a complete protein — meaning they contain all nine essential amino acids. Protein is vital in assisting proper growth and development, maintaining muscle mass and strength, and repairing the body after injury or surgery.
Selenium. Daily recommended selenium intake for adults age 14 and over ranges from 60 to 75 micrograms (μg). One poached egg contains 21 μg of selenium — about one-third of what’s recommended daily. Selenium is a powerful antioxidant that also boosts the body’s immune system.
Zinc. Zinc helps with growth, wound healing, blood formation and maintenance of healthy tissue. It’s recommended that adults 14 and over get at least 7 mg and no more than 14 mg of zinc each day. Two eggs contain 1.2 mg of zinc or 8.5% of the daily recommended intake.
B Vitamins. Vitamins B2, B6, and B12 can all be found in eggs. The body is unable to store B vitamins, so they must be consumed daily. Any excess B vitamins are flushed out in the urine, so it’s difficult to get too much. B vitamins are incredibly important; they aid in converting protein, carbohydrates, and fat into energy, promoting healthy blood and nerves, and making DNA.
Folate. The amount of folate someone needs depends on age and gender; pregnant and breastfeeding women need the most folate in their diet. As with B vitamins, the body needs folate to make DNA and other genetic material. This nutrient is also important in helping cells divide. Two eggs contain 46 μg of folate.
Vitamin A. Vitamin A is instrumental in proper growth and eye health. Two eggs contain 130 μg of Vitamin A. That amounts to 14% of the daily recommended intake.
Iodine. Adults age 14 and over should get 150 μg of iodine a day because iodine is essential in making sure the thyroid works correctly. One egg contains 20% of the daily recommended intake of iodine.
Vitamin D. Vitamin D is important for bone health. The older you get, the more Vitamin D you need. It’s recommended that people get 5 μg per day until age 50. Then, the recommended intake is 10 μg per day, and 15 μg per day after age 70. Vitamin D is found in the yolk of the egg, and one egg contains roughly 1.2 μg of vitamin D.
An Egg-cellent Food
Eggs are a great addition to a healthy diet. But, as with other animal-derived proteins, it’s important not to overdo it. If you’re worried your diet may be deficient in key vitamins and minerals, talk to your doctor, a dietitian or a nutritionist.




