What’s the Difference Between Psoriasis and Eczema?

Psoriasis and eczema are skin conditions that have similar symptoms and can be difficult to tell apart. In fact, even doctors sometimes find it challenging to determine which condition is present.
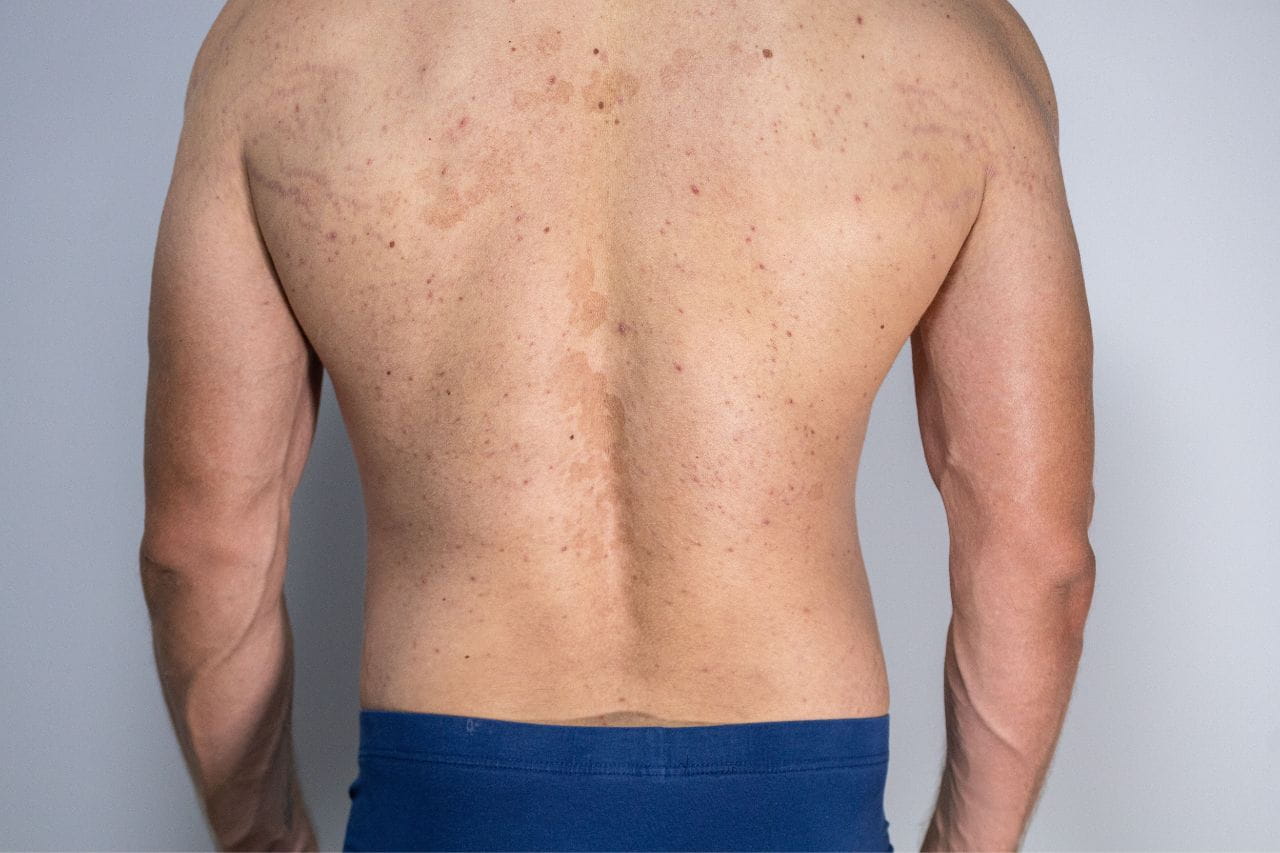
Psoriasis is an autoimmune issue in which skin cells grow more quickly than they normally would. As a result, dead cells build up into silvery-white scales. In addition, skin in the affected area becomes red, irritated and itchy.
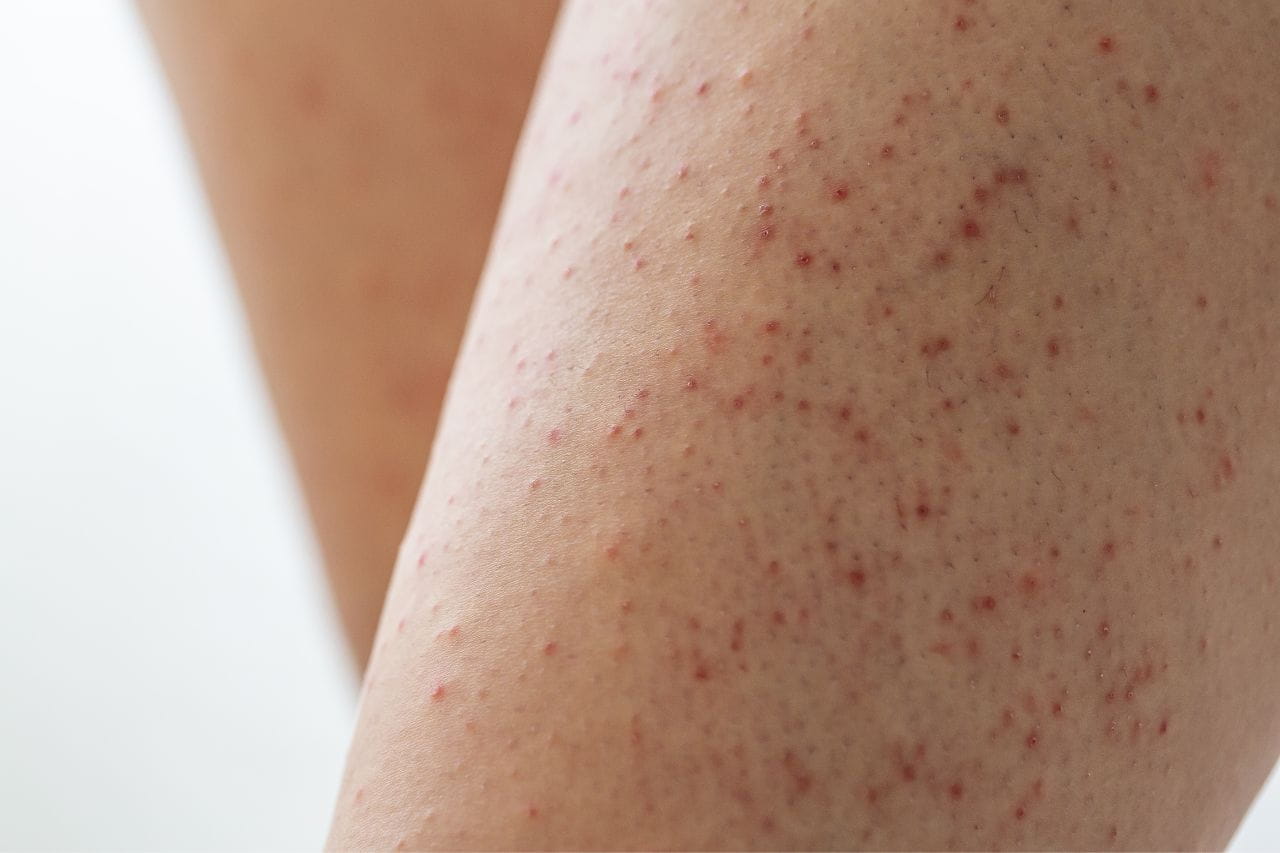
Eczema can be caused by a wide variety of factors including family history and exposure to bacteria, allergens or other environmental irritants. It also produces red, inflamed, itchy skin.
While they’re similar in some aspects, psoriasis and eczema differ in characteristics like:
Location
Psoriasis commonly occurs in areas like the scalp, face, knees, elbows, lower back, palms, and soles of the feet. Eczema tends to appear on the inside surface of parts of the body that bend like the elbows and knees. It’s also common on the neck, wrists and ankles.
Appearance
Psoriasis causes raised, thickened areas of skin that are red or silvery and scaly. Eczema causes redness, inflammation and sometimes dark coloration of the skin. Affected areas may also be crusty or scaly, and they may ooze.
Sensation
Psoriasis itches, but people with the condition also describe a burning or stinging sensation. They may say it feels like being pricked or stung. The primary sensation with eczema is intense itching. It can cause people to scratch so vigorously that their skin bleeds.
Preventing and Treating Psoriasis and Eczema
Psoriasis may be associated with other health conditions like heart disease, diabetes or depression. Preventing or managing those conditions properly can help prevent psoriasis. If the condition does develop, there are both topical treatments (emollients and corticosteroids, for example) and systemic measures like including various types of medication.
Eczema is often associated with dry, sensitive skin. Keeping the skin moisturized can help prevent eczema. As with psoriasis, there are both topical and systemic treatments. They include emollients and corticosteroids for mild to moderate cases. Moderate to severe eczema is treated using drugs that affect the immune system. Light therapy is also used in some cases.
Learn More About Dermatological Conditions Like Psoriasis and Eczema at Baptist Health
Have questions about a skin condition? Make an appointment to talk with a doctor at Baptist Health.