Type 1 & Type 2 Diabetes

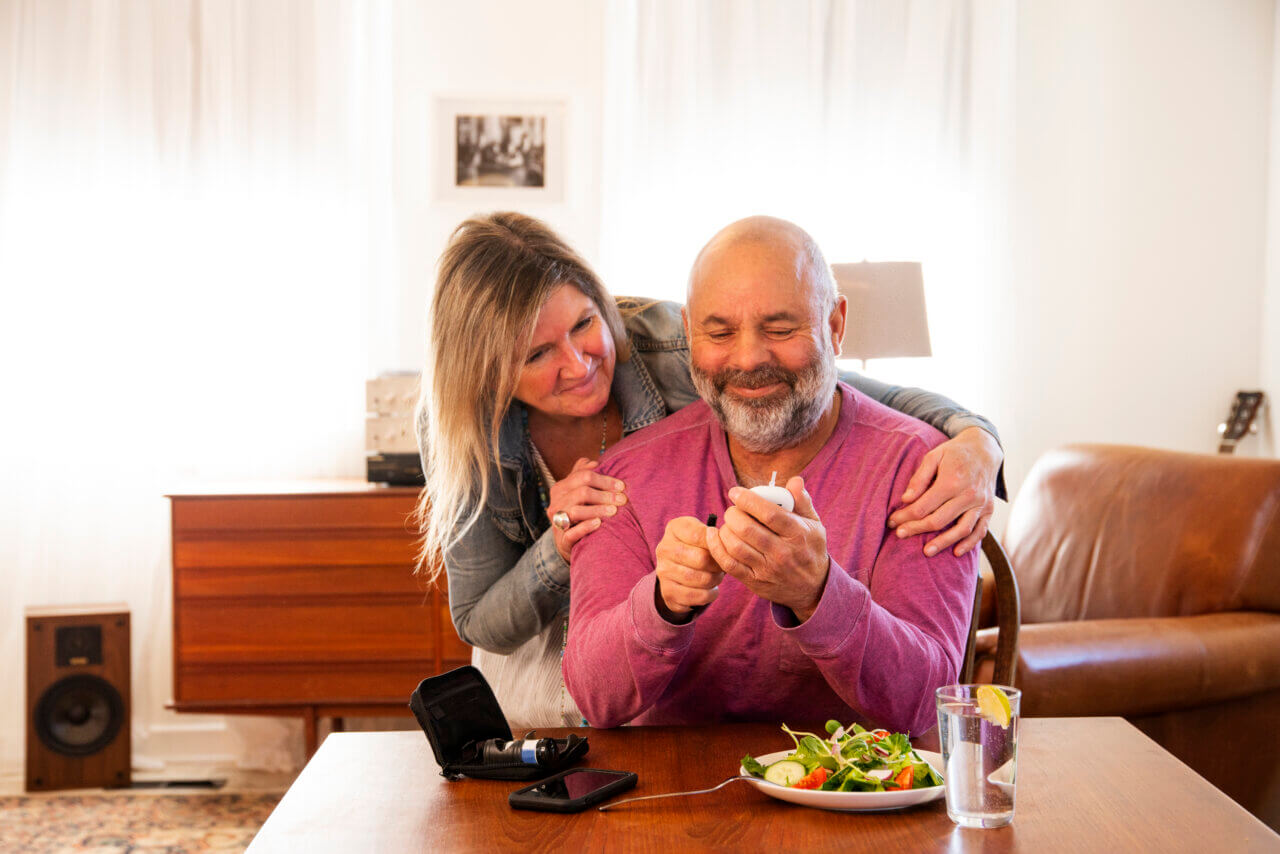
More than 30 million Americans are living with either type 1 or type 2 diabetes in the United States and while similar, the two diseases are not exactly the same. Knowing the differences between the two types of diabetes is important in managing your health and recognizing the risk factors and warning signs for each.
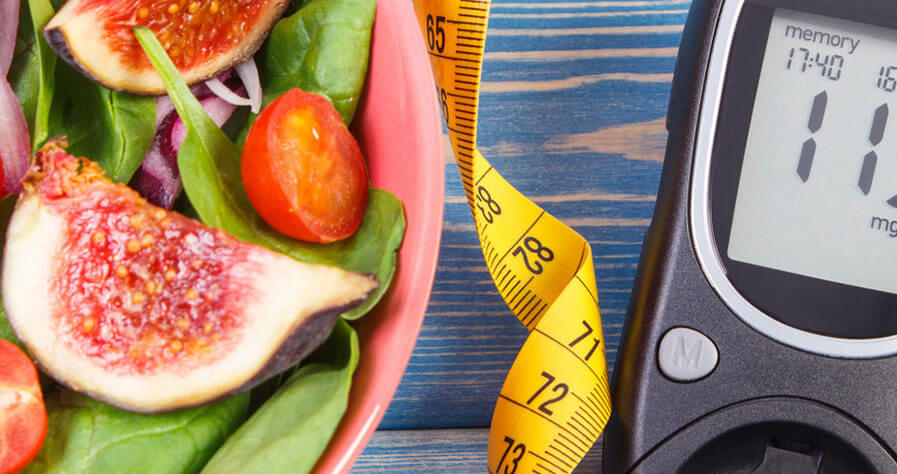
In type 1 diabetes, one’s immune system fights the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas thus inhibiting the body from producing the hormone naturally. Conversely, those with type 2 diabetes simply have a hard time producing enough or using insulin effectively. Those with type 1 diabetes have to take insulin supplements for the rest of their lives while type 2 diabetes can be treated through various health and diet management options.
Although anyone can develop type 1 diabetes, it is most commonly diagnosed at a younger age while type 2 diabetes is typically, although not always, found in older individuals, those who are overweight, or people with a family history of the disease. Type 2 diabetes is also more common than type 1 diabetes and accounts for 90-95% of diabetes cases in adults.
If you feel you may be predisposed to developing diabetes of any kind or believe your health history or lifestyle increases your risk, consult with your primary care physician as soon as possible. When left untreated or unmanaged, diabetes can lead to serious health problems such as stroke, kidney disease, heart disease, or even death.
Baptist Health offers a number of resources on diabetes education, self-management, and professional care options for you or your family.